Potential Energy
Potential Energy: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Potential Energy, Zero Level of Potential Energy, Position Dependence of Conservative Force and its Potential Energy, Spring Forces, Work Done by Spring Force & Energy Stored in Spring etc.
Important Questions on Potential Energy
A conservative force of () acts on a body of mass . The change in potential energy of the body due to the force, when it undergoes a displacement is
The variation of potential of a body moving along axis varies with the position as shown in the figure.The body is in equilibrium state in
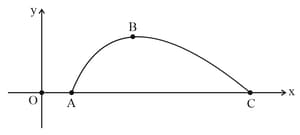
For the situation shown in the figure, horizontal spring and the spring connecting blocks and are light. The blocks and are of same mass . The pulley is smooth and fixed. The accelerations of and just after cutting the horizontal spring are
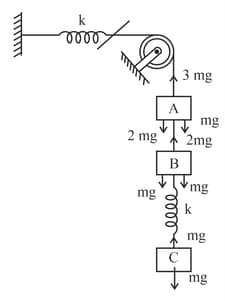
The force exerted by a special compression device is given as function of compression as for , where is the maximum possible compression and is a constant. The force exerted by the device under compression is maximum when compression is:
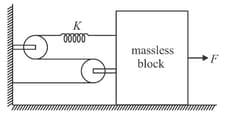
In the given diagram system is in equilibrium. If applied force is doubled how much distance, the mass less block will more towards right before new equilibrium is achieved.
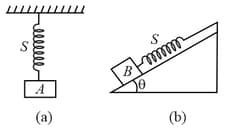
As shown in the figure, an iron block of volume is attached to a spring of unstretched length and hanging to the ceiling of a roof. The spring gets stretched by . This block is removed and another block of iron of volume is now attached to the same spring and kept on a frictionless incline plane of inclination. The distance of the block from the top along the incline at equilibrium is
Two blocks and of equal mass are arranged as shown with springs and . Spring is pulled with force . Acceleration of block is towards right at an instant. If is suddenly removed at this instant, the instantaneous acceleration of and will be (assume no friction)
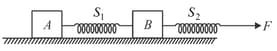
A bead of mass moves along a smooth fixed ring in a gravity free region. The ring has radius . The bead is attached to a spring of force constant and natural length . The other end of the spring is fixed to a point on the ring. At an instant shown in the figure when length of spring was , force applied by the ring on the bead was zero. Rate of change of speed of the bead at this instant will be
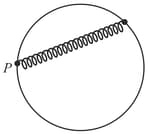
A particle of mass is attached with a spring of stiffness . When block is at it moves with maximum speed. The block moves with while passing through . Find out the coordinates in where it's velocity will be zero.
A spring long is stretched by the application of a force. If force required to stretch the spring through , then work done in stretching the spring through is
When, two ends of an ideal spring are pulled apart increasing its length it produces force equal to at its ends. At a point of its length from one end, the force is
Two blocks with mass and respectively are connected by a stretched spring of negligible mass as in figure. When the two blocks are released simultaneously the initial acceleration of is westward. The acceleration of is:
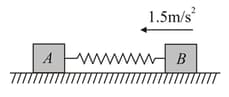
The spring constant of the spring of a gun is newton/meter. The spring has been compressed meter from its normal position and a bullet of mass has been put in the barrel. If the friction is negligible then on firing the gun, the bullet shall have a velocity of
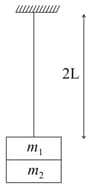
From a fixed support , hangs an elastic string of negligible mass and natural length . Masses and attached at the lower end, elongate the string to . When is removed gently, is able to bounce back to . The ratio is (assume that the string does not obstruct the motion of )
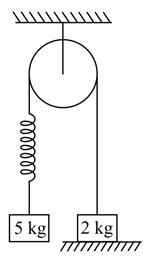
The system shown in the figure is released from rest. Pulley and spring are massless and friction is absent everywhere. The speed of block when block leaves the contact with ground is
is the force constant of a spring. The work done in increasing its extension from to will be
A body is falling from a height h. After it has fallen a height h/2, it will possess_____.
Water stored in a dam possesses_____.
A car is accelerated on a levelled road and attains a velocity 4 times of its initial velocity. In this process the potential energy of the car_____.
